Acinetobacter baumanii, and its species, continue to pose a significant threat to intensive care units, the definitive confirmation of these organisms is reliant on DNA sequencing and molecular amplification tests, which are costly and require skilled technicians.
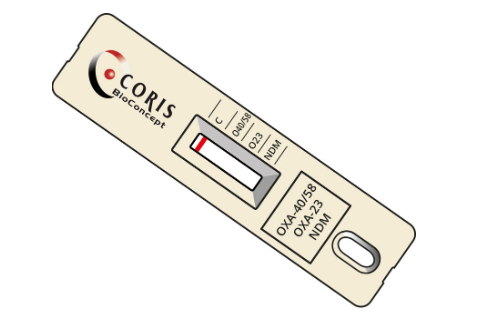
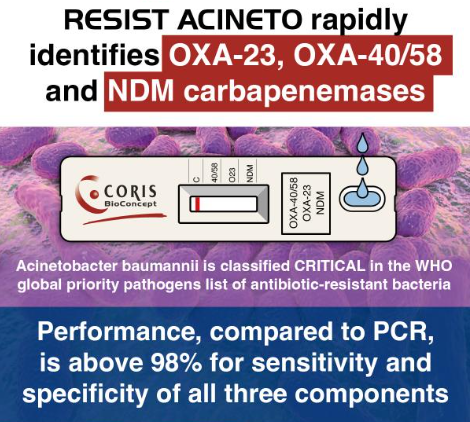
The RESIST ACINETO (K15R13) is a unique LFA for the rapid identification of OXA-23, OXA-40/58, NDM carbapenemases, and their variants. The development of new rapid diagnostic tests to track antimicrobial resistance patterns is considered as one of the priority core actions by international experts and health authorities.
The RESIST ACINETO (K15R13) is a unique LFA for the rapid identification of OXA-23, OXA-40/58, NDM carbapenemases, and their variants. The development of new rapid diagnostic tests to track antimicrobial resistance patterns is considered as one of the priority core actions by international experts and health authorities.
Early recognition of carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter spp
✔ Assist in effective management care
✔ Prevention of the establishment of endemic strains of carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter spp
✔ Allows rapid implementation of strategies to control transmission
✔ Assist in effective management care
✔ Prevention of the establishment of endemic strains of carbapenemase-producing Acinetobacter spp
✔ Allows rapid implementation of strategies to control transmission
Background
Acinetobacter baumannii is an important opportunistic and multidrug-resistant Gram negative bacteria responsible for nosocomial infections in health facilities.
If left untreated, this infection can lead to septicemia and death. The carbapenem hydrolyzing oxacillinases (OXAs) are the most commonly reported carbapenem resistance determinants in Acinetobacter spp., particularly in A. baumannii, with OXA23 as the most prevalent carbapenem-resistance determinant observed in these isolates.
OXA-40 (=24) and OXA-58 are also often encountered, and recently Acinetobacter spp. harbouring OXA’s together with NDM have emerged, particularly because of mobile genetic elements co-harbouring NDM and OXA encoding genes.
Mobile genetic elements (incl. plasmids) constitute reservoirs for horizontal transmission of these resistance factors. Detection of these resistance factors, not only in resistant species but also in carrier species, is therefore of paramount importance in the control of antibiotic resistance in the hospital.
Nowadays, definitive confirmation of OXA-23, OXA-40, OXA-58, and NDM relies on molecular amplification analysis and DNA sequencing. These tests are expensive and can only be performed in a dedicated environment and by skilled staff, hence limiting their more generalized usage. The development of new rapid diagnostic tests to track antimicrobial resistance patterns is considered as one of the priority core actions by international experts and health authorities.
The RESIST ACINETO test aims at a rapid identification of the OXA-23, OXA-40/58 and NDM carbapenemases (and variants of the OXA-23, 40 and 58 groups) to ensure effective treatment of patients and prevention of the spread of Acinetobacter spp. carbapenemase carriage, especially in hospitals.
Acinetobacter baumannii is an important opportunistic and multidrug-resistant Gram negative bacteria responsible for nosocomial infections in health facilities.
If left untreated, this infection can lead to septicemia and death. The carbapenem hydrolyzing oxacillinases (OXAs) are the most commonly reported carbapenem resistance determinants in Acinetobacter spp., particularly in A. baumannii, with OXA23 as the most prevalent carbapenem-resistance determinant observed in these isolates.
OXA-40 (=24) and OXA-58 are also often encountered, and recently Acinetobacter spp. harbouring OXA’s together with NDM have emerged, particularly because of mobile genetic elements co-harbouring NDM and OXA encoding genes.
Mobile genetic elements (incl. plasmids) constitute reservoirs for horizontal transmission of these resistance factors. Detection of these resistance factors, not only in resistant species but also in carrier species, is therefore of paramount importance in the control of antibiotic resistance in the hospital.
Nowadays, definitive confirmation of OXA-23, OXA-40, OXA-58, and NDM relies on molecular amplification analysis and DNA sequencing. These tests are expensive and can only be performed in a dedicated environment and by skilled staff, hence limiting their more generalized usage. The development of new rapid diagnostic tests to track antimicrobial resistance patterns is considered as one of the priority core actions by international experts and health authorities.
The RESIST ACINETO test aims at a rapid identification of the OXA-23, OXA-40/58 and NDM carbapenemases (and variants of the OXA-23, 40 and 58 groups) to ensure effective treatment of patients and prevention of the spread of Acinetobacter spp. carbapenemase carriage, especially in hospitals.
|
|
|