Sections
History and Development - Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs), Carbapenemases
Rapid detection of Carbapenemases from Blood Cultures
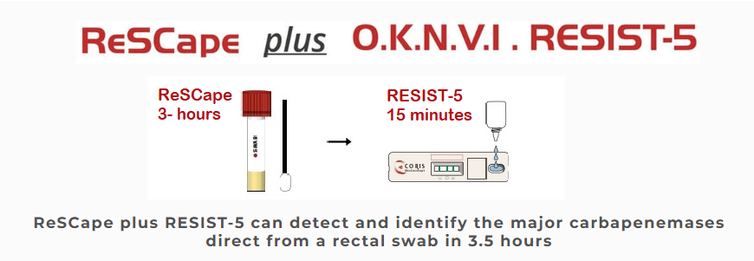
Rectal Screening for Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales
History and Development - Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs), Carbapenemases
Rapid detection of Carbapenemases from Blood Cultures
Rectal Screening for Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales
Antimicrobial Resistance - History and Development
Origins and Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance
This review presents the salient aspects of antibiotic resistance development over the past half-century, with the oft-restated conclusion that it is time to act
PubMed2010
This review presents the salient aspects of antibiotic resistance development over the past half-century, with the oft-restated conclusion that it is time to act
PubMed2010
The Antibiotic Resistance Crisis
The antibiotic resistance crisis has been attributed to the overuse and misuse of these medications, as well as a lack of new drug development by the pharmaceutical industry due to reduced economic incentives and challenging regulatory requirements.
PubMed 2015
The antibiotic resistance crisis has been attributed to the overuse and misuse of these medications, as well as a lack of new drug development by the pharmaceutical industry due to reduced economic incentives and challenging regulatory requirements.
PubMed 2015
Antibiotic resistance - World Health Organization (WHO)
Antibiotic resistance is accelerated by the misuse and overuse of antibiotics, as well as poor infection prevention and control. Steps can be taken at all levels of society to reduce the impact and limit the spread of resistance.
WHO 2020
About Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance is an urgent global public health threat, killing at least 1.27 million people worldwide and associated with nearly 5 million deaths in 2019.
CDC 2022
Antibiotic-resistant infections fell in 2020 for first time since 2016, but UKHSA warns drop likely temporary
New UKHSA data shows that bloodstream infections dropped in 2020 for the first time since 2016 but remain at a higher level than 6 years ago,the decline was largely driven by a reduction in recorded bloodstream infections overall, likely due to less social mixing, enhanced hand hygiene and changes to healthcare access and delivery.
November 2021
New UKHSA data shows that bloodstream infections dropped in 2020 for the first time since 2016 but remain at a higher level than 6 years ago,the decline was largely driven by a reduction in recorded bloodstream infections overall, likely due to less social mixing, enhanced hand hygiene and changes to healthcare access and delivery.
November 2021
Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs)
Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs): treatment, prevention, surveillance
How to prevent the spread of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing E. coli and Klebsiella - and treatment options..
Gov.UK 2013
EUCAST guidelines for detection of resistance mechanisms Version 1.0 December 2013
The recommended strategy for the detection of ESBLs in Enterobacteriaceae is based on non-susceptibility to indicator oxyiminocephalosporins, followed by phenotypic (and in some cases genotypic) confirmation tests.
EUCAST 2013
EUCAST guidelines for detection of resistance mechanisms Version 2.0 July 2017
Cefpodoxime is the most sensitive individual indicator cephalosporin for detection of ESBL production and may be used for screening. However, it is less specific than the combination of cefotaxime (or ceftriaxone) and ceftazidime (13, 14) and only the latter compounds are used in the confirmation testing.
EUCAST 2017
Carbapenemases
Tackling antimicrobial resistance 2019 to 2024: addendum to the UK's 5-year national action plan
GOV.UK Published 16 May 2022
GOV.UK Published 16 May 2022
- more specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time-bound (SMART)
- reflect lessons learned from the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic
- reflect progress that has already been made against ambitions to reduce antibiotic prescribing in food-producing animals
- work towards new sector targets
Rapid detection of Carbapenemases from Blood Cultures
Improving the blood culture pathway – Executive summary A national review of blood culture pathway processes to support better antimicrobial stewardship and improved patient safety
NHS England Version 1, 29 June 2022
'Optimising the blood culture pathway is essential in ensuring the best outcomes for patients with sepsis and in providing the most effective antimicrobial stewardship programs.' '..improved speed of detection of positive blood cultures, resulting in: improved antimicrobial stewardship (AMS), improved outcomes from sepsis, early identification of a specific organism, supporting a more accurate infection diagnosis, guiding specific investigations and further management, and early identification of infection control and public health implications.'
NHS England Version 1, 29 June 2022
'Optimising the blood culture pathway is essential in ensuring the best outcomes for patients with sepsis and in providing the most effective antimicrobial stewardship programs.' '..improved speed of detection of positive blood cultures, resulting in: improved antimicrobial stewardship (AMS), improved outcomes from sepsis, early identification of a specific organism, supporting a more accurate infection diagnosis, guiding specific investigations and further management, and early identification of infection control and public health implications.'
UK GOV Policy Paper Tackling antimicrobial resistance 2019 to 2024: addendum to the UK's 5-year national action plan
Link - http://bit.ly/3WJahRx Published 16 May 2022
'Halve healthcare associated Gram-negative bloodstream infections (GNBSIs)'
'introduce 4 new commitments to reduce urinary tract infections (UTIs), in support of the national action plan ambition to halve healthcare associated Gram-negative bloodstream infections (GNBSIs) by 2024. These commitments reflect the fact that UTIs are a common pathway to GNBSI,'
'Establish the IPC and care standards developed in Scotland (and already adopted in Wales) as the national standards in England, to be measured annually by the regulators.' Commitment retained
Link - http://bit.ly/3WJahRx Published 16 May 2022
'Halve healthcare associated Gram-negative bloodstream infections (GNBSIs)'
'introduce 4 new commitments to reduce urinary tract infections (UTIs), in support of the national action plan ambition to halve healthcare associated Gram-negative bloodstream infections (GNBSIs) by 2024. These commitments reflect the fact that UTIs are a common pathway to GNBSI,'
'Establish the IPC and care standards developed in Scotland (and already adopted in Wales) as the national standards in England, to be measured annually by the regulators.' Commitment retained
How are patients screened for CPE in Scotland?
National Infection Prevention and Control Manual
Toolkit for the early detection, management and control of carbapenemase- producing Enterobacteriaceae in Scottish acute settings
National Infection Prevention and Control Manual
Toolkit for the early detection, management and control of carbapenemase- producing Enterobacteriaceae in Scottish acute settings
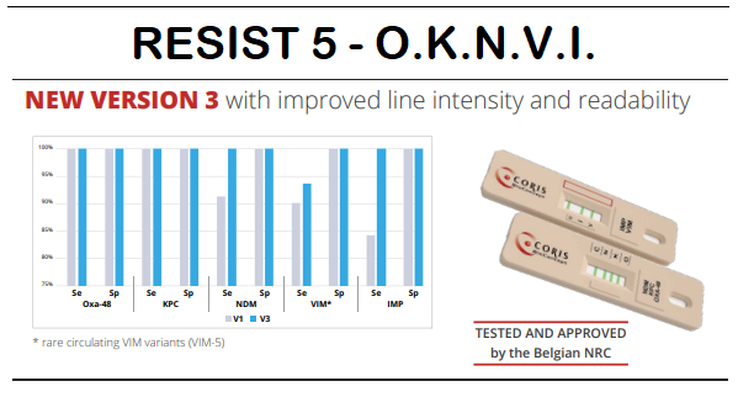
Application and clinical impact of the RESIST-4 O.K.N.V. rapid diagnostic test for carbapenemase detection in blood cultures and clinical samples
Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021
'The RDT provided reliable results in less than 30 min, both on culture-grown colonies as well as on pellets from positive blood cultures. Most importantly, carbapenemase detection always led to a treatment modification'
Blood Culture Pathway - Royal College of Pathologists
Bulletin 201 January 2023
antimicrobial resistance (AMR) must be a core part of clinical leadership and Trust governance
Bulletin 201 January 2023
antimicrobial resistance (AMR) must be a core part of clinical leadership and Trust governance
UK Standards for Microbiology Investigations Investigation of blood cultures (for organisms other than Mycobacterium species)
Bacteriology | B 37 | Issue no: 8.2 | Issue date: 05.09.19 |(Under Review)
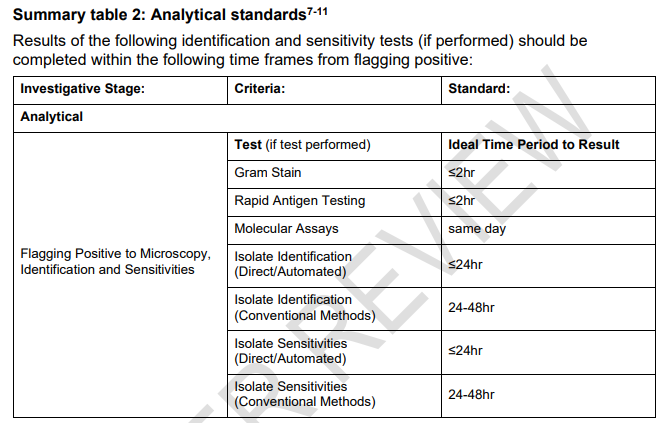
Summary table 2: Analytical standards7-11 Results of the following identification and sensitivity tests (if performed) should be completed within the following time frames from flagging positive:
Bacteriology | B 37 | Issue no: 8.2 | Issue date: 05.09.19 |(Under Review)
Summary table 2: Analytical standards7-11 Results of the following identification and sensitivity tests (if performed) should be completed within the following time frames from flagging positive:
Rectal Screening for Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales
Framework of actions to contain carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales
UK Health Security Agency September 2022
The framework sets out a range of measures, that if implemented well, will help health and social care providers minimise the impact of CPE. These include:
• active patient admission screening of risk groups
• rapid detection of patients colonised or infected with CPE, with appropriate surveillance systems to enable ongoing monitoring
UK Health Security Agency September 2022
The framework sets out a range of measures, that if implemented well, will help health and social care providers minimise the impact of CPE. These include:
• active patient admission screening of risk groups
• rapid detection of patients colonised or infected with CPE, with appropriate surveillance systems to enable ongoing monitoring
Framework of actions to contain carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales - 2.5 Screening swabs
UK Health Security Agency September 2022
'Rectal specimens are most sensitive for detecting the carriage of antibiotic resistant Enterobacterales (14). If a screening sample is required, the ability of the lab to detect the presence of CPE can be optimised by:
• a rectal swab, making sure faecal material and/or discolouration is visible on the swab (a stool specimen if a rectal swab is not feasible or acceptable)
• a wound swab and or a urine sample (if catheterised)'
UK Health Security Agency September 2022
'Rectal specimens are most sensitive for detecting the carriage of antibiotic resistant Enterobacterales (14). If a screening sample is required, the ability of the lab to detect the presence of CPE can be optimised by:
• a rectal swab, making sure faecal material and/or discolouration is visible on the swab (a stool specimen if a rectal swab is not feasible or acceptable)
• a wound swab and or a urine sample (if catheterised)'
Lateral flow immunochromatographic assay for rapid screening of faecal carriage of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae.
J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018
lateral immunochromatography performed directly from rectal swab samples could represent a cost-effective alternative with a reduced turnaround time.
J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018
lateral immunochromatography performed directly from rectal swab samples could represent a cost-effective alternative with a reduced turnaround time.
Reduction in the detection time of OXA-48, OXA-163 and KPC carbapenemases performed with a novel immunochromatographic lateral flow assay from 2-hour-old cultures (early cultures).
F. Pasteran et al poster 27th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 2017
By comparing the 40/41 Adeno-Strip test results with the whole PCR procedure, no one sample has been misdiagnosed. The high simplicity and rapidity of the method let us decide to use this diagnostic tool for our routine analysis.
F. Pasteran et al poster 27th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 2017
By comparing the 40/41 Adeno-Strip test results with the whole PCR procedure, no one sample has been misdiagnosed. The high simplicity and rapidity of the method let us decide to use this diagnostic tool for our routine analysis.
Four-Hour Immunochromatographic Detection of Intestinal Carriage of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae: a Validation Study
Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2021
'our protocol is a rapid, easy-to-perform, and low-cost method allowing for the accurate detection of the digestive colonization with CPE in less than 4 h after sampling without any requirement for specific equipment. In this sense, it offers advantages compared to molecular biology and overnight culture on selective plates.'
'Sensitivity and specificity for C-PGNB detection were 97.7% .... and 100% .....'
Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2021
'our protocol is a rapid, easy-to-perform, and low-cost method allowing for the accurate detection of the digestive colonization with CPE in less than 4 h after sampling without any requirement for specific equipment. In this sense, it offers advantages compared to molecular biology and overnight culture on selective plates.'
'Sensitivity and specificity for C-PGNB detection were 97.7% .... and 100% .....'