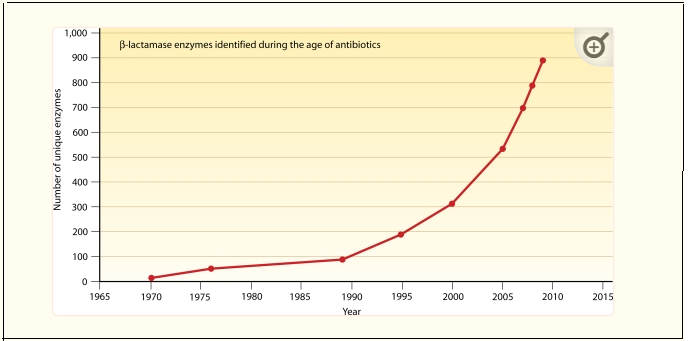
Beta Lactam Resistance - History and Development
Origins and Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance
PubMed 2010
This review presents the salient aspects of antibiotic resistance development over the past half-century, with the oft-restated conclusion that it is time to act
LINK
The Antibiotic Resistance Crisis
PubMed 2015
The antibiotic resistance crisis has been attributed to the overuse and misuse of these medications, as well as a lack of new drug development by the pharmaceutical industry due to reduced economic incentives and challenging regulatory requirements.
LINK
Antibiotic resistance - World Health Organization (WHO)
WHO 2020
Antibiotic resistance is accelerated by the misuse and overuse of antibiotics, as well as poor infection prevention and control. Steps can be taken at all levels of society to reduce the impact and limit the spread of resistance.
LINK
About Antimicrobial Resistance
CDC 2022
Antimicrobial resistance is an urgent global public health threat, killing at least 1.27 million people worldwide and associated with nearly 5 million deaths in 2019.
LINK
Antibiotic-resistant infections fell in 2020 for first time since 2016, but UKHSA warns drop likely temporary
UKHSA November 2021
New UKHSA data shows that bloodstream infections dropped in 2020 for the first time since 2016 but remain at a higher level than 6 years ago,the decline was largely driven by a reduction in recorded bloodstream infections overall, likely due to less social mixing, enhanced hand hygiene and changes to healthcare access and delivery.
LINK
PubMed 2010
This review presents the salient aspects of antibiotic resistance development over the past half-century, with the oft-restated conclusion that it is time to act
LINK
The Antibiotic Resistance Crisis
PubMed 2015
The antibiotic resistance crisis has been attributed to the overuse and misuse of these medications, as well as a lack of new drug development by the pharmaceutical industry due to reduced economic incentives and challenging regulatory requirements.
LINK
Antibiotic resistance - World Health Organization (WHO)
WHO 2020
Antibiotic resistance is accelerated by the misuse and overuse of antibiotics, as well as poor infection prevention and control. Steps can be taken at all levels of society to reduce the impact and limit the spread of resistance.
LINK
About Antimicrobial Resistance
CDC 2022
Antimicrobial resistance is an urgent global public health threat, killing at least 1.27 million people worldwide and associated with nearly 5 million deaths in 2019.
LINK
Antibiotic-resistant infections fell in 2020 for first time since 2016, but UKHSA warns drop likely temporary
UKHSA November 2021
New UKHSA data shows that bloodstream infections dropped in 2020 for the first time since 2016 but remain at a higher level than 6 years ago,the decline was largely driven by a reduction in recorded bloodstream infections overall, likely due to less social mixing, enhanced hand hygiene and changes to healthcare access and delivery.
LINK
Molecular Mechanisms, Epidemiology, and Clinical Importance of β-Lactam Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae
International Journal of Medical Sciences 2020
'the overuse of these antibiotics has contributed to select β-lactam-resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolates, so that β-lactam resistance is nowadays a major concern worldwide. The production of enzymes that inactivate β-lactams, mainly extended-spectrum β-lactamases and carbapenemases, can confer multidrug resistance patterns that seriously compromise therapeutic options.,
International Journal of Medical Sciences 2020
'the overuse of these antibiotics has contributed to select β-lactam-resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolates, so that β-lactam resistance is nowadays a major concern worldwide. The production of enzymes that inactivate β-lactams, mainly extended-spectrum β-lactamases and carbapenemases, can confer multidrug resistance patterns that seriously compromise therapeutic options.,
About Antimicrobial Resistance
CDC 2022
Antimicrobial resistance is an urgent global public health threat, killing at least 1.27 million people worldwide and associated with nearly 5 million deaths in 2019.
About Antimicrobial Resistance
CDC 2022
Antimicrobial resistance is an urgent global public health threat, killing at least 1.27 million people worldwide and associated with nearly 5 million deaths in 2019.